Global leader in powertrain trusted by customers Hwashin Precision Co., Ltd.
It refers to an eco-friendly car that operates by driving a motor using electricity obtained by reacting hydrogen with oxygen in the air instead of a gasoline internal combustion engine. It is a vehicle powered by a fuel cell that does not emit exhaust gas and pollutants because it does not have an engine. The car is equipped with fuel cell stacks, motors, batteries, and hydrogen tanks.

It is completely pollution-free because only water is generated during operation by supplying hydrogen using a compressed hydrogen tank/liquid hydrogen tank. However, there are disadvantages such as increased vehicle volume due to tank installation, instability of hydrogen, and difficulty in establishing hydrogen supply infrastructure.
Carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides are generated when methanol is decomposed by decomposing methanol to make and supply hydrogen, but they are much less than conventional fossil fuel vehicles. This method has the advantage of being able to use the existing fuel supply infrastructure.
Electricity generation, the core of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, drives motors with electricity generated by the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen through catalysts. In other words, when water is electrolyzed, oxygen is produced at the positive (+) electrode and hydrogen is produced at the negative (-) electrode. Conversely, when water is made using hydrogen, electricity is generated in the process.
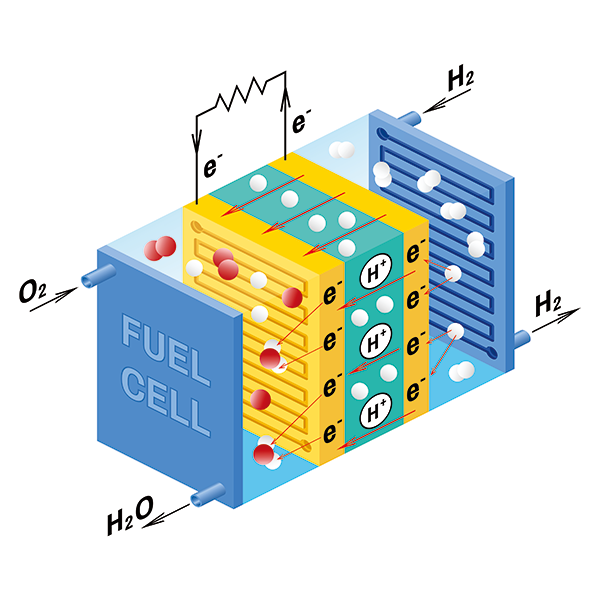
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are equipped with fuel cell stacks, motors, batteries, hydrogen tanks, heat and water management devices, air conditioners, power conversion devices, and high-pressure valves. Among them, a stack is a fuel cell body in which hundreds of cells are stacked in series, and is a point where electricity is generated by a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. The unit cell of the stack is composed of a membrane electrode assembly (MEA) and a separator. Among them, MEA is divided into an anode and a cathode, which are catalyst electrodes composed of a polymer electrolyte membrane that moves hydrogen ions and a platinum catalyst applied to both sides of the electrolyte membrane.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles emit little pollutants, so there is little environmental pollution, and long-distance driving is possible with a small amount of fuel. However, in the event of a serious vehicle accident, hydrogen is likely to explode, and economic feasibility is pointed out as a disadvantage due to high energy consumption in generating hydrogen.
Comparing hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles not only have a short charging time of around 5 minutes, but also have a long travel distance after charging. However, there is a disadvantage that production costs are high and vehicle prices are high. Electric cars are much cheaper than hydrogen cars and have relatively built infrastructure such as charging. However, the time for electric charging is relatively long, ranging from 20 to 30 minutes, and the driving distance is much shorter than that of hydrogen cars.
| Sortation | a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle | an electric car |
|---|---|---|
| Power | Fuel cell (the raw material is hydrogen) | electricity |
| Advantage |
|
|
| Weakness |
|
|
Daimler Chrysler introduced NECAR1 (New Electric Car) using hydrogen storage fuel cells in 1994 as the world's first company to develop hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Currently, most automakers, including Daimler Chrysler, Ford, GM, Toyota, and Hyundai, are investing in fuel cell vehicle development and are competing to dominate the market. In addition, General Motors (GM) developed a gasoline-powered fuel cell in 2001 and attracted attention by unveiling its fuel cell concept car, AUTONOMY, at the North American International Motor Show held in Detroit in January 2002.
In Korea, Hyundai succeeded in piloting the Santa Fe fuel cell vehicle, which was powered by pure fuel cells, in 2001, and succeeded in driving for 300 miles in a row with competitors such as Daimler Chrysler, Ford, GM, and Honda at the 2002 Fuel Cell Road Rally held in California in September 2002. And Hyundai Motor Company first introduced the Tucson ix at the Geneva Motor Show in March 2010 and exported it to Europe for the first time as it succeeded in mass-producing the world's first hydrogen car in March 2013.